Merus's Preclinical Bispecific Zeno Demonstrates Efficacy in Cancer Models
Dutch oncology company Merus has announced preclinical data for zenocutuzumab (Zeno), their HER2xHER3 targeting humanized gG1 bispecific antibody. The data, presented at the American Association of Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2024, outlines effective results for the drug in cancer models with a high expression of neuregulin 1 (NRG1).
Merus's pipeline consists of bi- and tri- specific molecules for the treatment of cancers, which they call Biclonics® and Triclonics® respectively.
RELATED:
- WuXi Biologics and GSK Enter License Agreement for Bispecific Development
- The Bispecific Antibody Landscape
- T Cell Engagement and Activation: New Developments
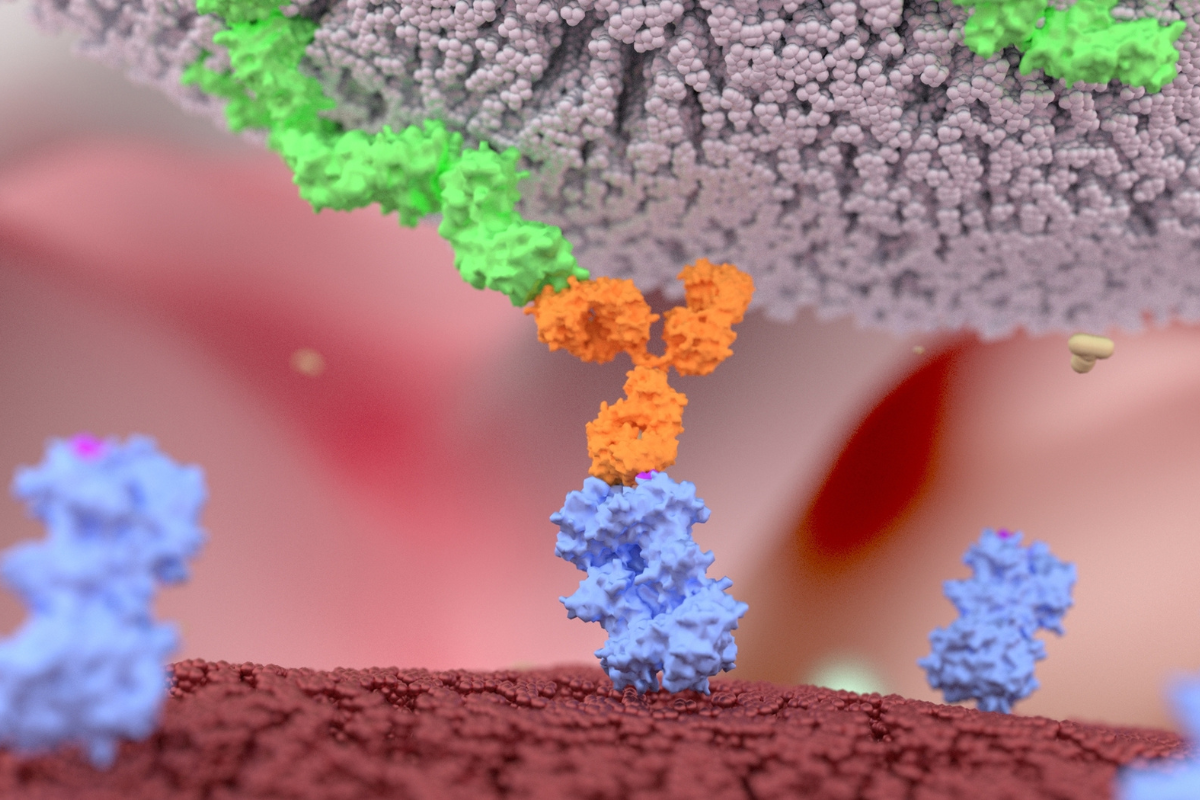
NRG1 is a ligand that docks to HER3 which in turn allows for the dimerization of HER2 and HER3. The interaction between HER3 and NRG1 also forms a tumour signalling pathway.
Zeno works by first docking to HER2, preventing it from heterodimerizing with HER3. Then, its other arm binds to HER3, which blocks its interaction with NRG1, thereby blocking the NRG1/HER3 tumour signalling.
Cecile Geuijen, Chief Scientific Officer at Merus said: "Zeno was selected utilizing unbiased assays to allow biology to teach us which is the best potential Biclonic®. Thereafter, we continue to learn more both preclinically and mechanistically, to identify where the molecule holds potential."
He continued: "In this study, we examined the efficacy of Zeno in preclinical models expressing high NRG1 levels and found evidence of anti-tumour activity in multiple tumour types."
The study involved 28 patient derived xenograft models including 21 different tumour types, all with high NRG1 expression. Seven of the models tested showed significant slowing of tumour growth.
Furthermore, Zeno was shown to inhibit N87 gastric cancer, HCC95 lung cancer, and SKBR-3 breast cancer cell line proliferation in models with a high rate of NRG1 expression. In the case of HCC95 lung cancer, Zeno blocked signalling pathways, interfering with tumour cell growth and survival.
Merus commented in their press release that: "These data show that Zeno is effective in tumour cell killing in vitro and in vivo in high NRG1 expressing cancer models representing multiple different tumour types."