Healthcare Data Platforms: Expert Tips on Integrating Digitalisation with Cell and Gene Manufacturing

In the cell and gene manufacturing sphere, automation is an increasingly central tenet of manufacturing across both bigger companies and smaller biotechs. Recent conversation has focused on how - and to what extent - digital tools and automation can be implemented into the day-to-day processes that form the broader manufacturing pipelines in healthcare data platforms. Automated data interpretation methods can extract insights from sequencing or imaging data more rapidly than humans can manually.
By applying digitalisation techniques such as deep learning to interpret large volumes of data, researchers can better keep up with the ever-increasing rate at which data is being generated. A panel at Cell UK 2022 discussed some of the best approaches to improving data access and data sharing for cell and gene therapy manufacture. Significant challenges presently exist in the upscaling of curative therapy manufacturing.
A cloud-first digital transformation has already proven to be of significant positive impact to cost, quality, and scale in other industries such as finance and commerce. With the correct framework in place, research teams can factor in predictions to better prepare resources and clinical sites post-manufacture, potentially getting treatments to patients earlier and saving more lives.
An Overview of Healthcare Data Platforms and Data Security
Increasingly, data access and data architecture is a focus for those working in or around cell and gene therapy manufacture. One challenge associated with a move towards digital solutions is the interaction between a hospital or healthcare clinic's research team and its IT department. Following a string of cyberattacks on institutions such as the NHS in the 2010s, most European healthcare providers have stringent IT safeguarding protocols to prevent external interference with patient data and information.
However, this has led to a significant amount of red tape concerning trial data sharing, which can hamstring collaborations with commercial partners across healthcare data platforms. Some of the issues faced by cell therapy teams in hospital environments have been simple but unexpected hurdles, such as static IP addresses not being allowed in the facility.
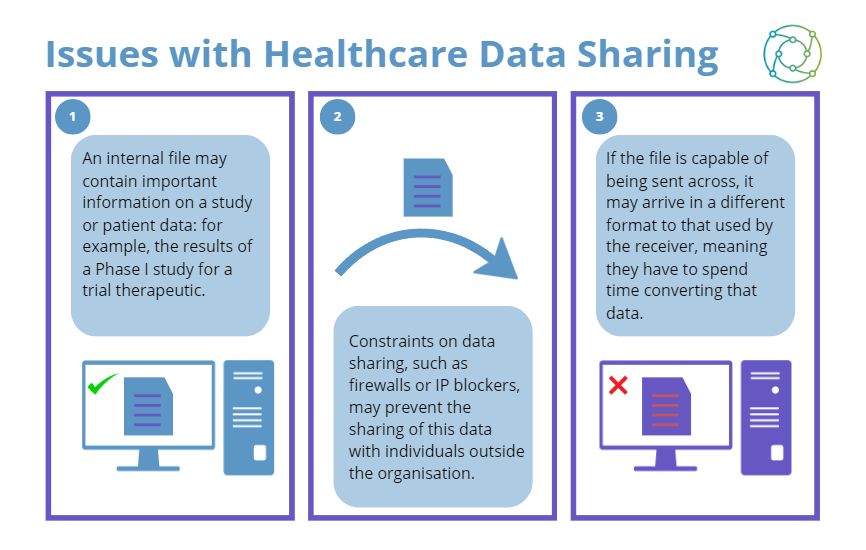
As a general rule of thumb, any collaboration will become more complex with the integration of additional operating systems. For example, if a hospital-based research team is working with a private company, the hospital may have a default operating system which is different to that of the private company. Converting data files to integrate across different platforms slows down the overall rate of development, and this has led some figures in the industry to call for a greater standardisation of data formats.
Healthcare Data Services and Data Provision
Given the difficulties and constraints that can arise when collaborating between healthcare providers and suppliers, making the right choice when it comes to a particular supplier for a particular aspect of the manufacturing process is paramount. Key approaches include clearly defining the absolute requirements or key functions for data, with those in the field advised to be open to new contacts on the market. Laying out internal requirements at the get-go also makes a big difference in addressing different requirements in hospital IT systems.
Another factor to consider when choosing a data solution is how flexible a system is for reconfiguration if a recipe changes. In terms of the technology changing this is always the case. Being able to incorporate a biomedical background and machine learning approach is key, since this allows for an integrated approach to interpolating data in a way that meets the needs of both the providers and end users.
Best-Practice Approaches to Process Digitalisation
Continuity in data interpretation and manipulation is equally important to monitor. Duygu Dikicioglu is an Associate Professor in Digital Bioprocessing and Biochemical Engineering at UCL, and explores how digital technologies can be applied to enable a smart data-driven approach to bioprocess design, control, and optimisation. She explained that researchers could assess the time and expenditure involved in integrating a new process versus the improvements it could provide in terms of reductions in cost of benefits to the patient.
- Applying metabolic modelling to cell and gene therapy manufacture
- Winning strategies for commercialisation and scale-up
- How could machine learning approaches reshape therapeutic development?
Many in the field are big advocates for moving towards automated systems at the first opportunity, as - viewed retrospectively - older systems are both a waste of materials and human resource time. “We're trying to promote and advocate for an electronic system as early as possible,” said one panellist. “Reducing human involvement by introducing an electronic system is critical, especially for the established processes.” They added that this had the impact of both reducing human error and allowing the time formerly dedicated to this process development to be spent on other aspects of the manufacturing process.
Implementing Data Management Architecture in Healthcare Data Platforms
Overall, there are two contexts for introducing a digital pipeline solution in healthcare data platforms. If the solution is well established, with other centres adopting it and a clear need to accelerate pathway development, then there is a concrete argument for conducting a cost-benefit analysis. Otherwise, interactions with colleagues and partners may lead to an apparent solution which is not yet fully-fledged, but whose proprietors are looking for a centre to trial it at lower cost.
Implementing data access and data management architecture in cell and gene therapy development in a healthcare environment should ensure that the method introduced is appropriate to the intended use case. Any developers looking to integrate digitalisation approaches into their pipelines should use an appropriate method for the problem being circumvented, and ensure the complexities of training staff in approaches are understood prior to introduction. Selecting a sensible architecture is key: rather than automating for the sake of automating, healthcare providers should assess the best approach well in advance.
Want to receive the latest industry announcements on cell manufacture and development? Sign up for our Cell series newsletter to get up-to-date news each month. If you'd like to know more about our upcoming 3D Cell Culture conference, visit our event website to download an agenda and register your interest.






