Inciting Rapid Standardisation in Cell and Gene Therapy Manufacturing

With the potential to revolutionise modern medicine, cell and gene-based therapeutics face a frantic pace of development and manufacturing. In fact, the global cell and gene therapy market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 27.8%, increasing from 3.8 billion USD in 2019 to 13.0 billion USD by 2024.
The untapped opportunities for improvement in the efficiency and robustness of gene pharmaceuticals mean the industry now turns its attention to establishing a synergistic form of process mapping. With the advent of next generation of cell and gene-based manufacturing technologies, exacting standards will be needed for regulators to keep up.
By mobilising a harmonised journey to manufacturing, with the help of distinct development strategies, streamlined quality control testing, and advanced scale-up processing measures, the gene therapy field can take a much-needed step towards industry standardisation. The foremost key players in the arena include Novartis, bluebird bio, Roche (Spark), Sangamo, RegenexBio, Bayer (AskBio and Bluerock), UniQure, Astellas to name a few.
Key Market Drivers:
In 2020 alone, the number of phase III clinical trials reached over 360, a figure that is set to rapidly increase over the coming few years. The exponential growth witnessed by the cell and gene therapy market can be attributed to several prominent drivers. In particular, the introduction of advanced therapies into the biopharmaceutical industry has helped reshape the treatment paradigm of numerous rare and life-threatening diseases.
The expanding cell and gene therapy arena has also seen the introduction of several new players and an increase in strategic alliances between pharmaceutical companies and contract manufacturers. In addition to this, the prevalence of Research and Development centres is forecast to further drive market growth, especially in North America.
Process mapping is integral to ensuring compliance at every phase of the development and commercialisation process.
But how exactly can regulators and developers alike adopt a standardised approach to delivering streamlined manufacturing to meet current market demand? And what can we expect from the future of gene-based therapy manufacturing?
Process Mapping: A Step Towards Industry Standardisation
Process mapping is integral to ensuring compliance at every phase of the development and commercialisation process. According to Jorgen Magnus, Strategic Program Lead of Cell and Gene Therapy at Bayer, “the industry standard in production technology for cell and gene therapy is still very immature.” The proper development of production technology has been side-lined due to the field's rapid growth.
“Because there has been no time, attention has consequently focused on jumping immediately to large scale manufacturing without adapting the process,” he continued. However, the problem with this approach is that developers only increase the volume and yield of drug candidates without actively implementing any changes. Concertation and focus on full-scale commercialisation often bypass process development (see figure. 1).
- Discover About Engineering Cell Lines for AAV Potency Assays
- What are the Foremost Challenges and Opportunities in Viral Vector-Based Gene Therapy
- Find out how to Overcome the Key Challenges of Gene Therapy Commercialisation
In particular, current technology for cell therapy is not suitable for large scale production. Due to the demand to, as Magnus puts it, “the supply for hundreds of patients with cell therapy, the solution is to number up the plates that are used for cell growth.” There are enormous disadvantages to this approach.
Such technologies are laborious, involving several manual steps. They can also be very expensive. Furthermore, insufficient development processes lead to variability and a poorly controlled process. “As such, we are eagerly awaiting for this leap in innovation to happen in producing perhaps suspension culture or an encapsulation system,” Magnus highlighted.
Why Create Process Mapping?
Technological innovations aside, the implementation of process maps offer a powerful management tool and strategy for the development and eventual rapid manufacturing of cell and gene therapies. Process maps represent example processes and unit operations to accelerate collaboration projects.
Magnus then spoke about his involvement in BioPhorum, an organisation that brings biopharmaceutical companies together to work on common topics and that has developed process maps for cell and gene therapy processes “to establish a common reference frame and educational tool to streamline process improvement and product commercialisation within the field.”
The rapid expansion and technological advances in the cell and gene therapy arena mean achieving a harmonised and thorough standard of practice requires a dynamic effort.
In particular, he explained how as it stands, there is no common standard for industrial production of cell and gene therapy that is publicly available. BioPhorum aims to bring together leaders working in the field and replace isolation with collaboration. Advantages of harnessing a united force via process mapping include a smoother transition to market and reduced patient treatment costs.
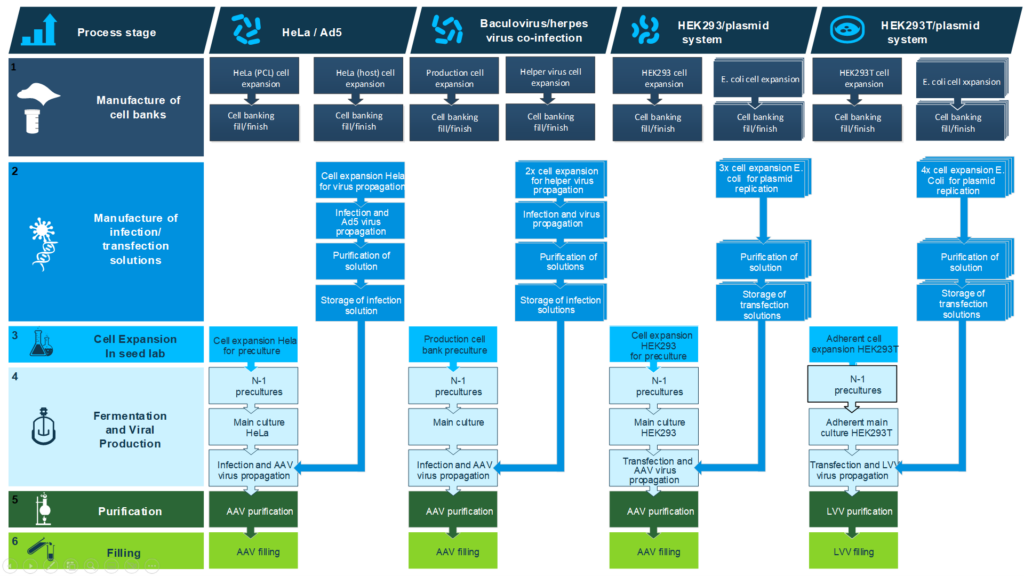
So far, leading companies such as AstraZeneca, Biogen, bluebird bio, Janssen, Lonza, Merck, REGENEXBIO, Roche Genentech, Sangamo Therapeutics, and Bayer have collaborated with BioPhorum. The syndicate has created a gene therapy procedure classifying different AAV processes to establish three distinct developmental processes (see figure. 2). BioPhorum found that with a broad representation, industry can progress further and achieve consensus on a more detailed level.
Future Outlooks:
The rapid expansion and technological advances in the cell and gene therapy arena mean achieving a harmonised and thorough standard of practice requires a dynamic effort. Critical factors in ensuring this include procuring a broad industry representation and harnessing automation to eliminate manual procedures.
Looking ahead to the next 10 years, better operational steps and quality control will be some of the expected trends seen in the rapid standardisation of cell and gene therapy. Whilst implementing consensus in development and manufacturing will be a rigorous and demanding task, introducing process mapping can bring cell and gene therapy into the future of medicinal production.
Want to find out more about the latest gene therapy news? Register now for Oxford Global's latest Gene Therapy Development & Manufacturing: In-Person event to find out more about optimised process strategies and technologies for the successful technical development and manufacture of advanced gene therapy products.







